India-Gulf Relations Strengthen Despite Regional Challenges
Amid ongoing regional conflicts and geopolitical tensions, the strategic partnership between India and Gulf countries continues to deepen and expand. Recent diplomatic engagements and economic collaborations showcase an increasingly resilient and multifaceted relationship that transcends traditional energy ties.
Diplomatic Engagements Reinforce Bilateral Ties
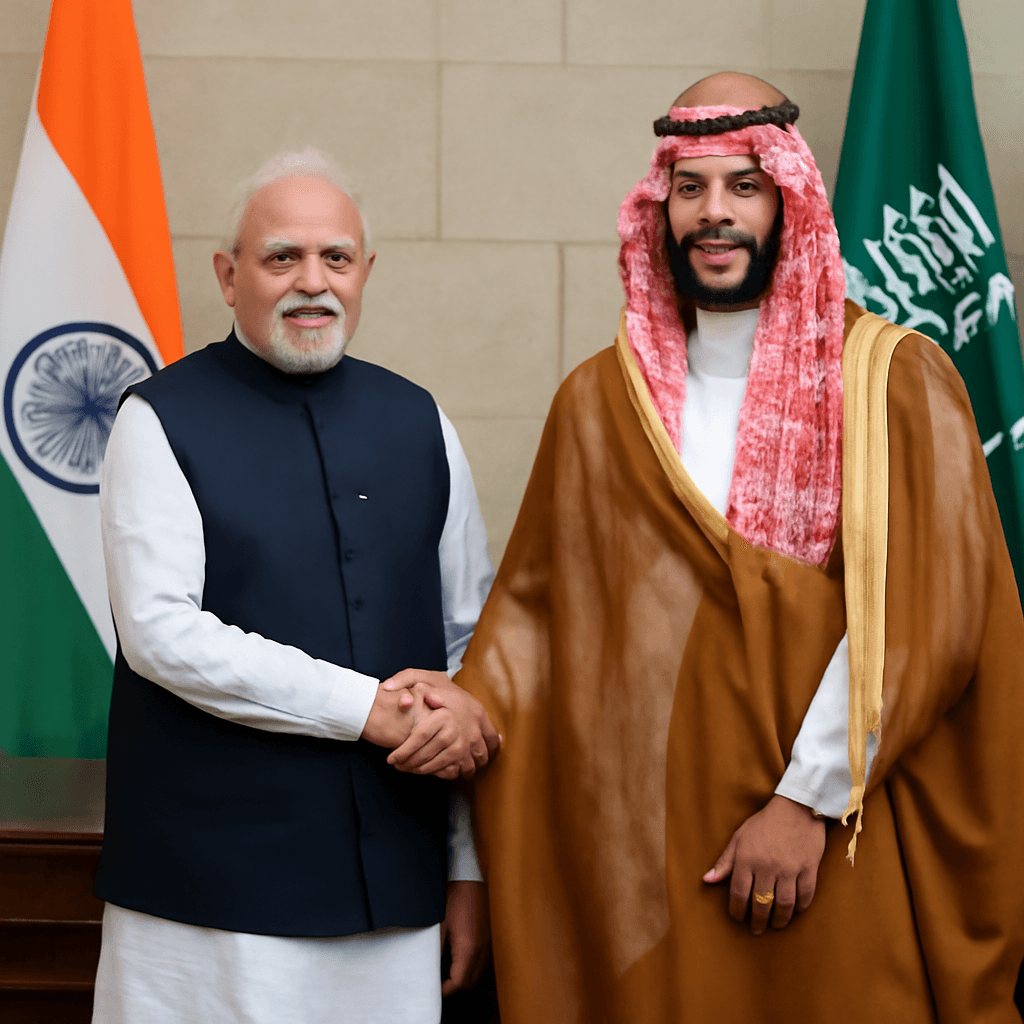
In April 2025, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi met Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman in Jeddah, marking Modi's third visit as prime minister to Saudi Arabia. This visit coincided with delicate regional events, including escalating India-Pakistan tensions and the conflict in Gaza, yet demonstrated continued commitment to India-Gulf rapprochement.
Over the past decade, the establishment of the India-Saudi Strategic Partnership Council has facilitated nearly 50 cooperation agreements in various sectors. A joint working group is actively pursuing a roadmap for Saudi investments in India, targeting an ambitious $100 billion influx, particularly in infrastructure and technology.
Beyond Oil: Expansion into Renewable Energy and Technology
India’s rapidly growing economy, with a GDP rising to $3.56 trillion in 2023 and a projected growth rate of 6.5% in 2024, is driving increased energy demand. India ranks as the world’s third-largest oil consumer, underscoring the strategic importance of Gulf energy supplies.
Simultaneously, there is a notable pivot toward sustainable energy collaborations. Saudi Arabia has committed $12 billion towards India's renewable energy, infrastructure, green hydrogen, solar power, and battery storage sectors. The India-Saudi Strategic Partnership Council now operates two distinct tracks: political/security and economic/investment, fostering a structured, multi-dimensional partnership.
Strengthening Defence Cooperation Across the Gulf
Defence partnerships between India and Gulf states—including Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Oman—have expanded through joint military exercises, intelligence sharing, and formal agreements.
- India-Saudi Arabia defence cooperation, initiated in 2014, supports military training, logistics, hydrography, and security collaboration. Their armed forces have engaged in multiple joint exercises, with the most recent Indian Army–Royal Saudi Land Forces staff talks held in April 2025.
- India's longstanding relationship with Oman includes a 1972 military protocol and a 2005 defence MoU. Notably, India secured naval access to Oman's strategic Duqm port in 2018 to enhance logistics and maintenance capabilities.
- The UAE recently advanced defence ties through coast guard and defence industry agreements formalised during official visits, aiming to scale cooperation in line with growing bilateral trade.
Trade Prospects: Free Trade Agreement Negotiations
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), comprising six Gulf states, intends to initiate free trade agreement (FTA) negotiations with India in 2025. This agreement aims to reduce trade barriers, facilitate economic integration, and boost collaboration in digital, industrial, and service sectors.
Bilateral trade between India and the GCC has grown steadily, with both sides viewing the FTA as pivotal in fortifying economic ties and enhancing investment opportunities. This move aligns with India's broader strategy to expand its network of FTAs to foster sustainable economic growth.
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
Unveiled at the 2023 G20 Summit, the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) seeks to connect India to Europe via the Arabian Peninsula and Israel, focusing on transport, digital infrastructure, and energy linkages.
IMEC represents a strategic initiative that enhances regional connectivity and counters competing infrastructure projects. While political tensions in the Middle East pose short-term challenges, the corridor remains a crucial framework for future trade and investment, supporting Gulf nations’ economic diversification efforts beyond oil.
People-to-People Connections Foster Mutual Trust
India sustains robust social and economic links with the Gulf, as approximately nine million non-resident Indians reside in GCC countries, constituting a quarter of India’s global diaspora population.
These communities contribute substantially through remittances and cultural exchange, forming a vital foundation for enduring bilateral cooperation. India's steady, long-term engagement strategy contrasts with more transactional global approaches, positioning it as a preferred partner in defense, trade, and diaspora relations.
Conclusion
Despite regional unrest and complex geopolitical dynamics, India-Gulf relations have attained unprecedented strategic depth. Through diversified investments, strengthened defence collaborations, trade negotiations, and robust people-to-people connections, this partnership is poised to grow stronger, underpinning economic growth and regional stability for decades to come.