National Guard Mobilizes in Washington DC Following Presidential Directive
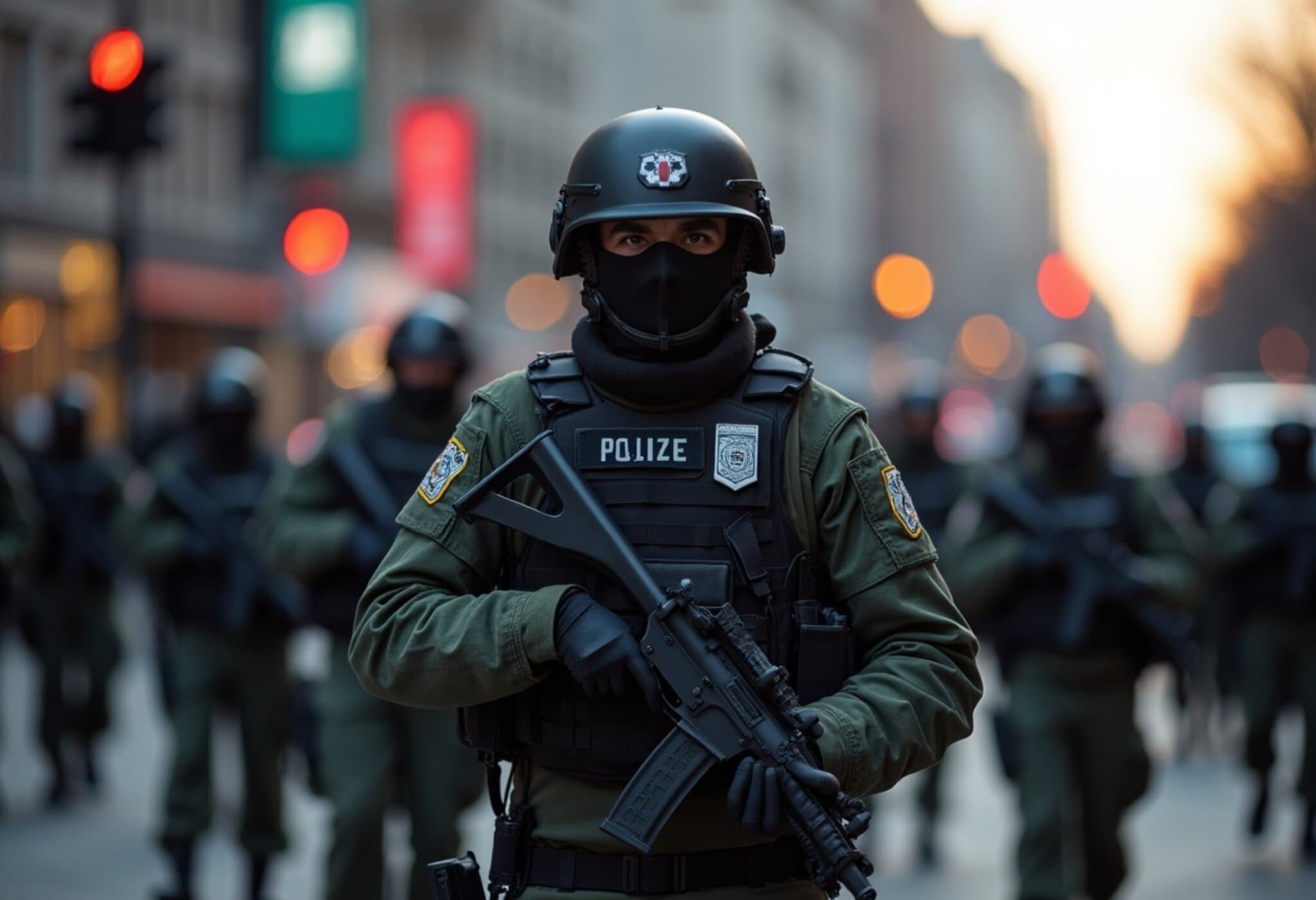
In a move stirring significant debate, the US National Guard has begun deploying in Washington DC, responding to an executive order from President Donald Trump aimed at curbing a recent rise in violent crime within the capital. This deployment represents a rare federal intervention in the city’s law enforcement operations, highlighting escalating tensions between local and federal authorities over public safety strategies.
Role and Responsibilities of the National Guard Troops
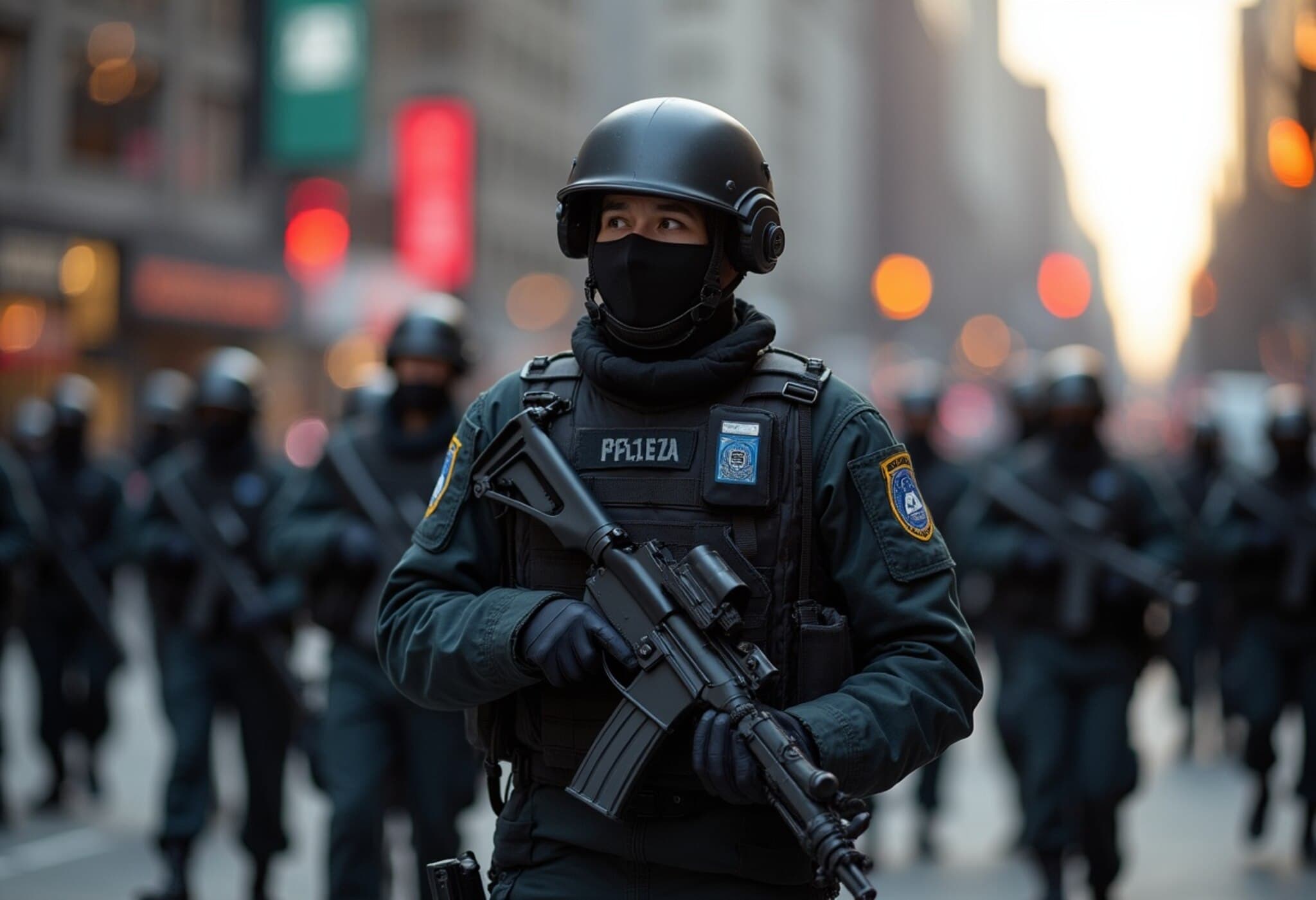
Over 800 National Guard personnel have assembled near the US Capitol, clad in military attire and prepared to coordinate with local law enforcement agencies. Contrary to initial assumptions, these troops primarily serve in supportive roles: managing crowds, securing perimeters, facilitating communication channels, and bolstering the visible law enforcement presence — all designed as deterrents to violent activity. Notably, an official source shared with NBC News that most National Guard members on the ground are not authorized to carry firearms during this operation.
A White House official explained, "The National Guard’s mission is to safeguard federal assets and provide a secure environment enabling police to perform arrests and suppress violent crime effectively."
Federal-Federal and Federal-Local Coordination
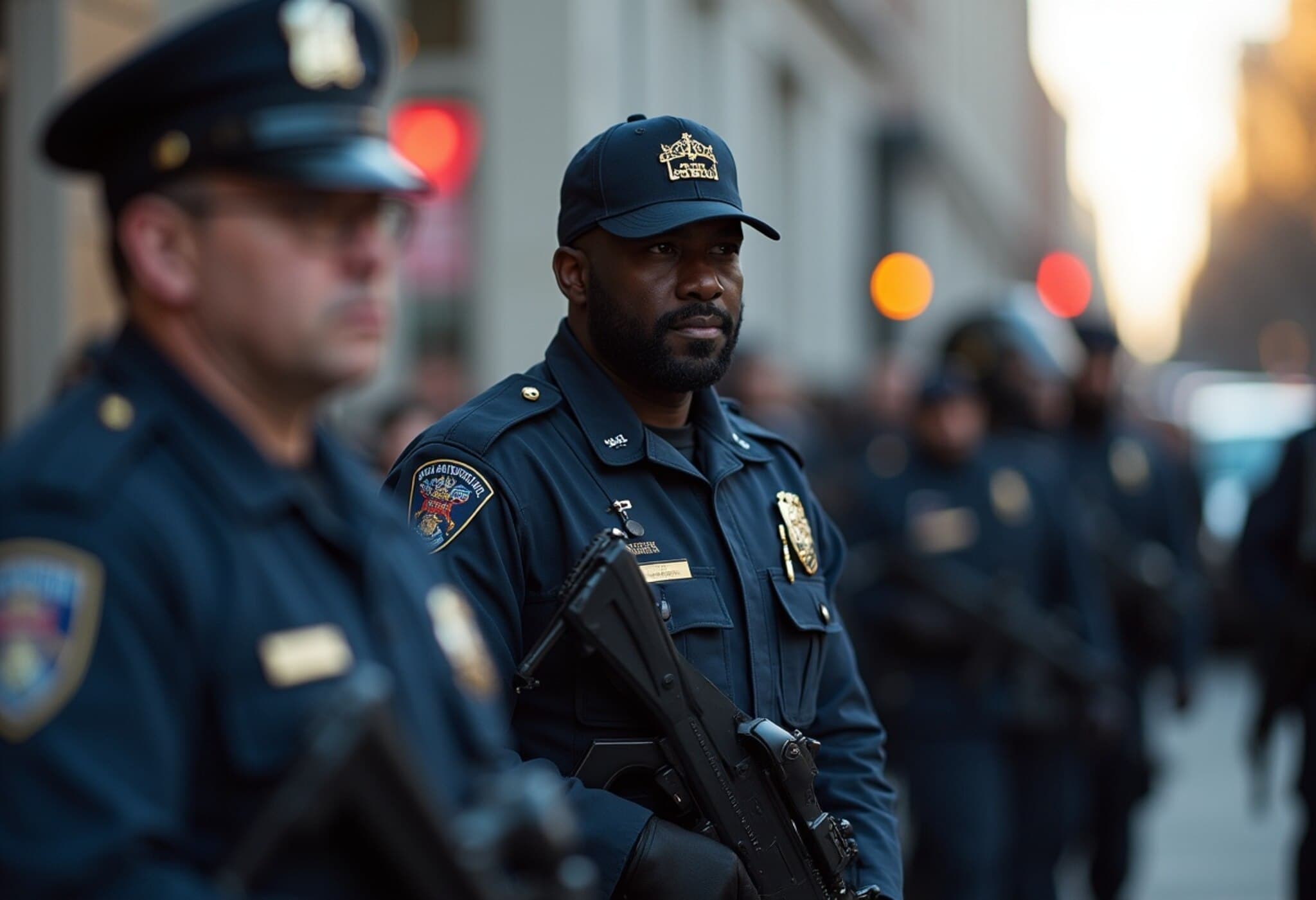
The federal takeover includes collaboration with the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), with its lead, Terry Cole, emphasizing a joint patrol approach where federal agents and city police work "hand in hand". Since this federal involvement began, over 20 arrests have been made, involving a range of offenses such as homicide, firearm violations, narcotics distribution, and reckless driving.
Local Political and Community Reactions
However, the intervention has been met with resistance from Washington DC’s Mayor, Muriel Bowser, a Democrat, who criticized the takeover as "the wrong way to do it". This disagreement underscores a broader debate about federal overreach and the appropriate balance between local autonomy and national security interests, especially significant in a city like Washington DC where crime rates and political sensitivities converge.
White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt stated that the federal control of the Metropolitan Police Department would be subject to reassessment after 30 days, emphasizing the administration’s intent to ensure "the most efficient operation possible."
Contextualizing the National Guard Deployment
Historically, the deployment of National Guard forces within US cities has been rare outside of extraordinary circumstances, such as civil unrest or natural disasters. This move comes at a time when urban crime rates have stirred national conversations on policing reform, public safety, and the role of federal authority. Experts caution that while additional manpower can temporarily curb violence, long-lasting solutions require community engagement, investment in social services, and police accountability frameworks.
Moreover, this federal involvement raises constitutional questions regarding Washington DC’s unique status—a federal district without full local governance autonomy—underscoring continued debates about its political representation and self-determination.
What Comes Next?
- Monitoring Efficiency: The White House’s 30-day review period will be critical in evaluating tangible outcomes and community impact.
- Law Enforcement Relations: The integration between federal and local policing agencies will require careful management to avoid jurisdictional conflicts and ensure effective crime-fighting cooperation.
- Political Dialogue: Constructive engagement among city leaders, residents, and federal officials can pave the way for sustainable security policies that respect civil liberties.
Editor’s Note
The National Guard’s presence in Washington DC marks a pivotal moment in federal-local law enforcement dynamics, one that prompts urgent reflection on how best to secure American cities amid rising crime without compromising democratic governance. As this story develops, readers should consider asking: Does stronger federal intervention undermine local choice, or can it serve as a necessary tool in extraordinary times? How will this balance shape the future of policing and community trust?