UK Launches Major Defense Spending Overhaul
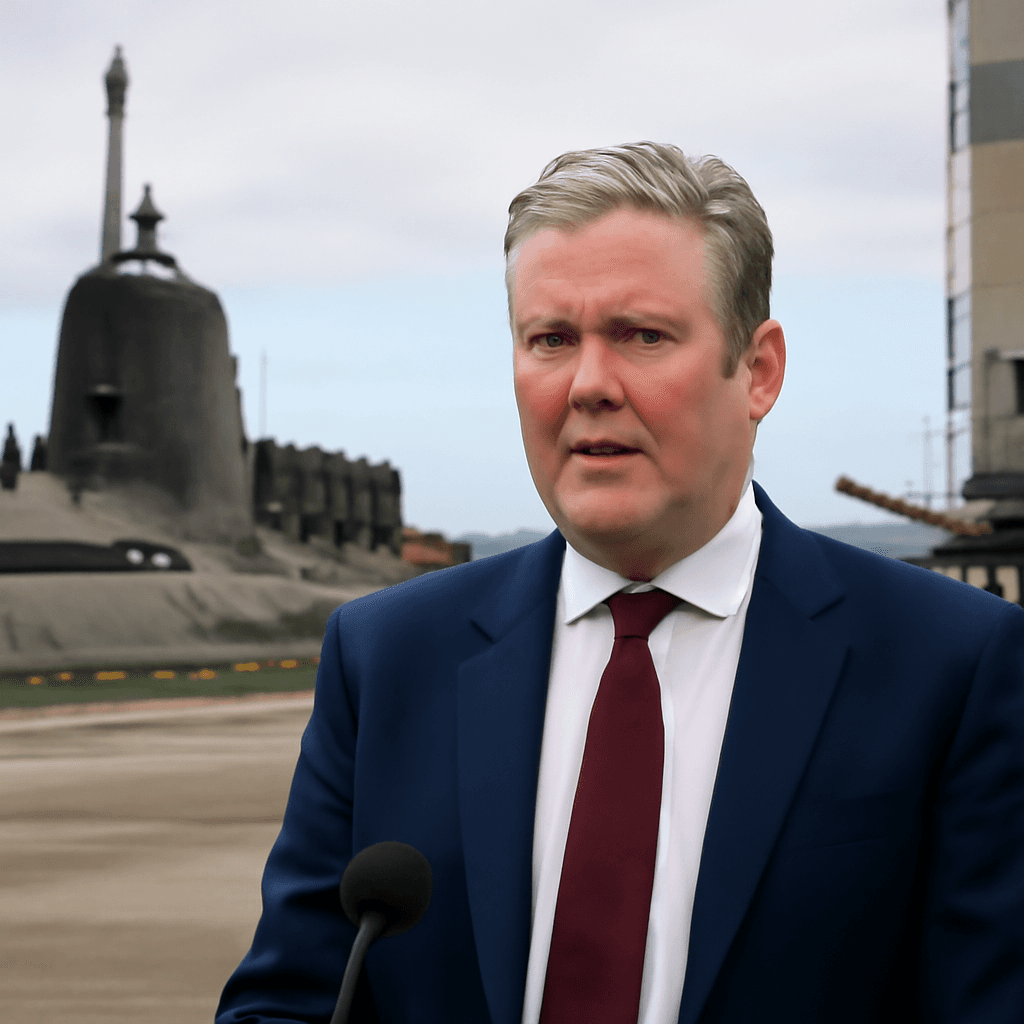
British Prime Minister Keir Starmer has unveiled a significant transformation of the United Kingdom's defense strategy, asserting that the nation is moving towards a state of "war-fighting readiness." This initiative comes amid escalating tensions and security threats in Europe, particularly attributed to growing Russian assertiveness.
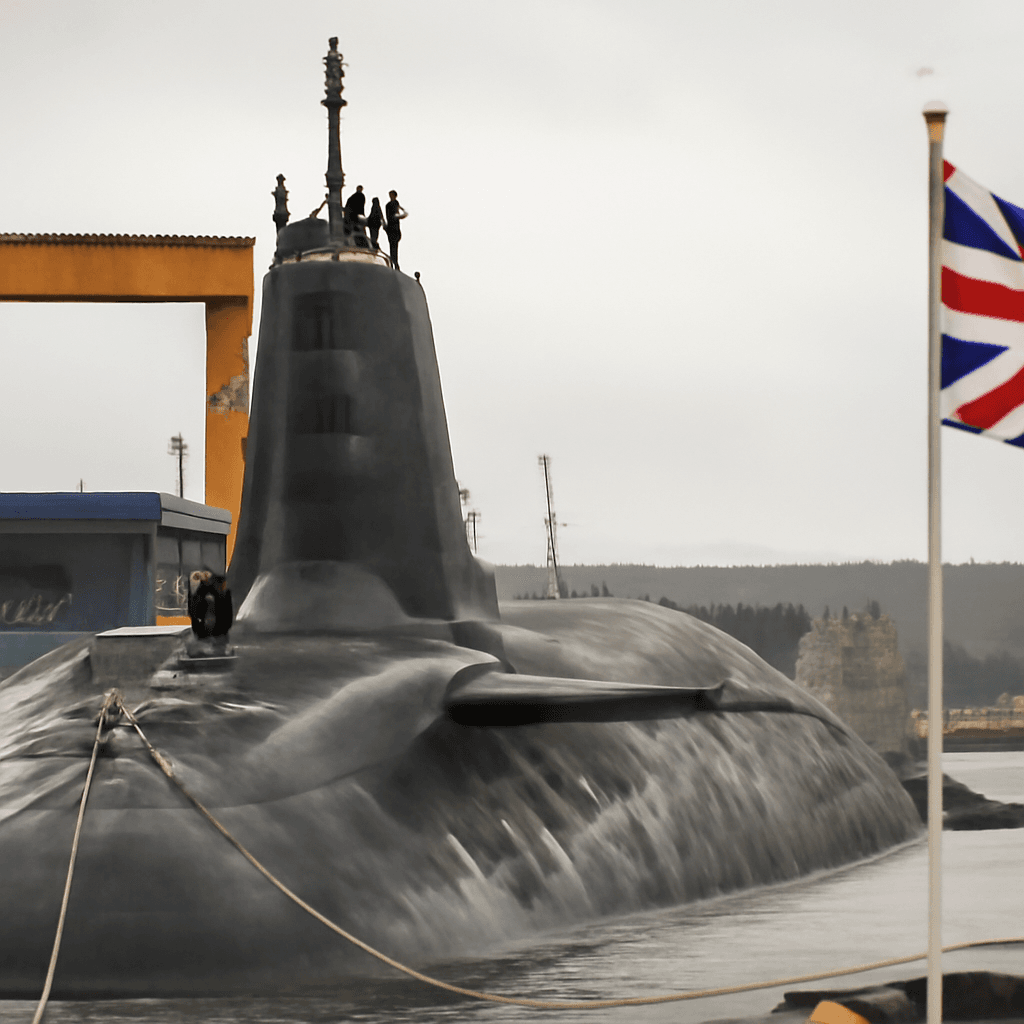
The government's strategic defense review includes plans to increase defense spending to 2.5% of GDP by 2027, with an ambition to further raise it to 3% by 2034, conditional upon economic and fiscal circumstances. As part of the overhaul, the UK will build 12 new nuclear-powered attack submarines and ramp up production of drones, missiles, and munitions to strengthen military capabilities.
Focus on NATO and European Security Cooperation
Starmer emphasized the UK's commitment to NATO, reiterating that defense policy will remain "NATO first." Strengthening the NATO alliance is a central priority, with the UK aiming to support collective defense commitments. NATO expects its 32 member states to increase defense spending and enhance security infrastructure by 2032.
Challenges and Criticism
While the proposed spending increases have been welcomed as responsive to the evolving geopolitical landscape, analysts caution these measures may be insufficient or delayed. The UK’s spending in 2024 was approximately 2.33% of GDP, already surpassing NATO's 2% target set in 2014, but critics note that a gradual increase might not meet the fast-changing demands of modern warfare.
Several NATO allies with higher defense budgets, like Lithuania (2.8% of GDP in 2024), have reacted skeptically toward the UK’s 2.5% target, urging a faster and more substantial commitment. Starmer, however, has declined to set a firm date for reaching the 3% spending goal, citing uncertainties in budget allocations.
Defense Sector Response and Strategic Implications
The European aerospace and defense sector responded positively to the UK's plans, reflected in a modest rise in the defense industry stock indices. According to experts, although the investment supports modernization efforts—such as nuclear warhead updates, submarine fleet expansion under AUKUS, and greater munition production—the overall impact will be gradual rather than transformative.
Military analysts argue that an increase to 2.5% GDP, while meaningful, is unlikely to enable a radical overhaul of the Armed Forces without significant restructuring or difficult decisions, such as early retirement of existing capabilities.
Fiscal Concerns and Economic Constraints
Fiscal limitations pose a significant challenge to the UK’s defense ambitions. Financial experts highlight the tight balance the government must maintain between enhancing military readiness and managing economic stability, public spending on social services, and maintaining investor confidence.
The Chancellor faces the complex task of accommodating increased defense allocations while satisfying public demand for investments in health, education, and infrastructure. Analysts warn of the possibility that the government may need to expedite its plans to reach 3% defense spending sooner than currently anticipated.
Conclusion: Balancing Ambition with Reality
The UK's new defense strategy reflects an urgent response to a rapidly shifting security environment in Europe. However, its success will depend on balancing ambitious military enhancements with fiscal realities and political will. As the UK commits to a strengthened defense posture, the coming years will test its capacity to deliver meaningful results in the face of evolving global threats.